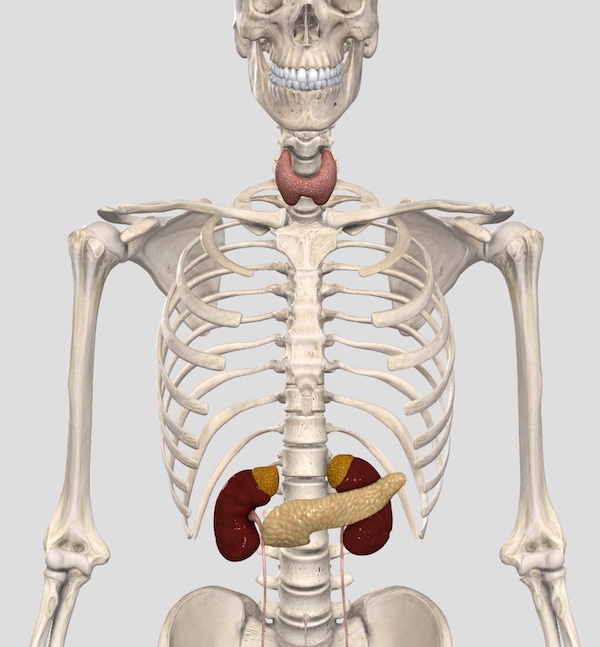
The Adrenal Glands
The two adrenal glands (also called the suprarenal glands) are situated in the abdomen, above the kidneys.
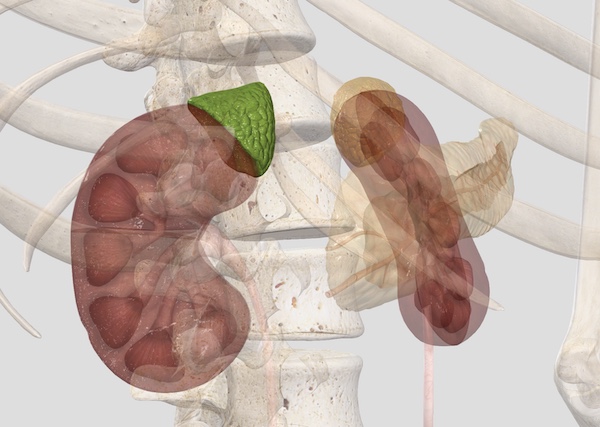
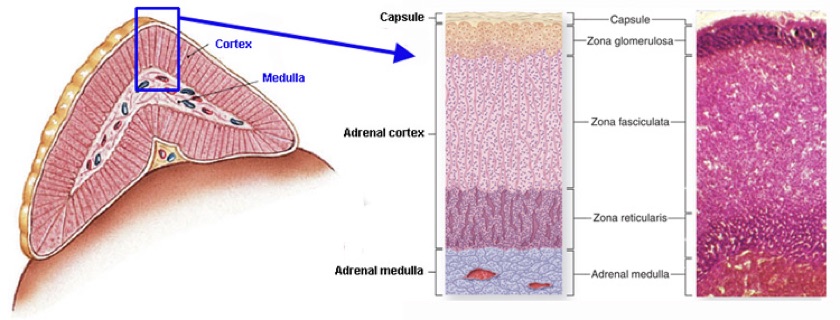
Each gland consists of an:
- Outer cortex – yellow in color
- Inner medulla – dark red or grey in color grey.
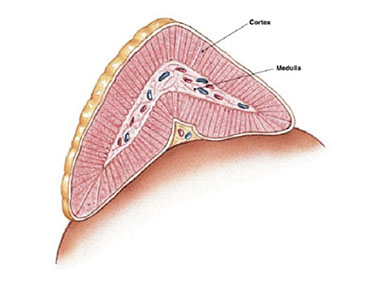
The cortex consists of three distinct zones:
- Zona Glomerulosa
- Zona Fasciculata
- Zona Reticularis
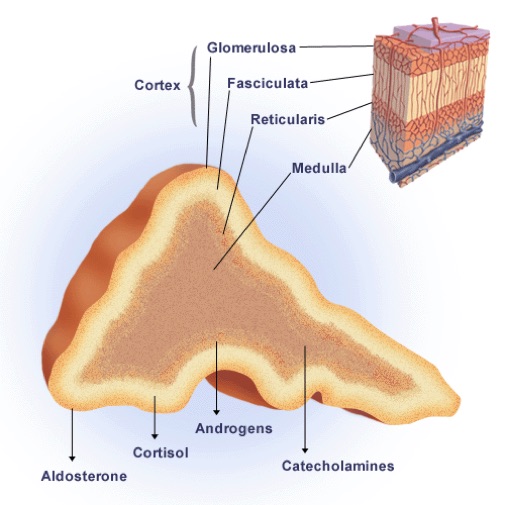
Each zone secretes different types of hormones:
- Zona Glomerulosa secretes mineralocorticoid (aldosterone)
- Zona Fasciculata secretes glucocorticoid (cortisol)
- Zona Reticularis secretes sex hormones (progesterone, estrogen precursors and androgens)
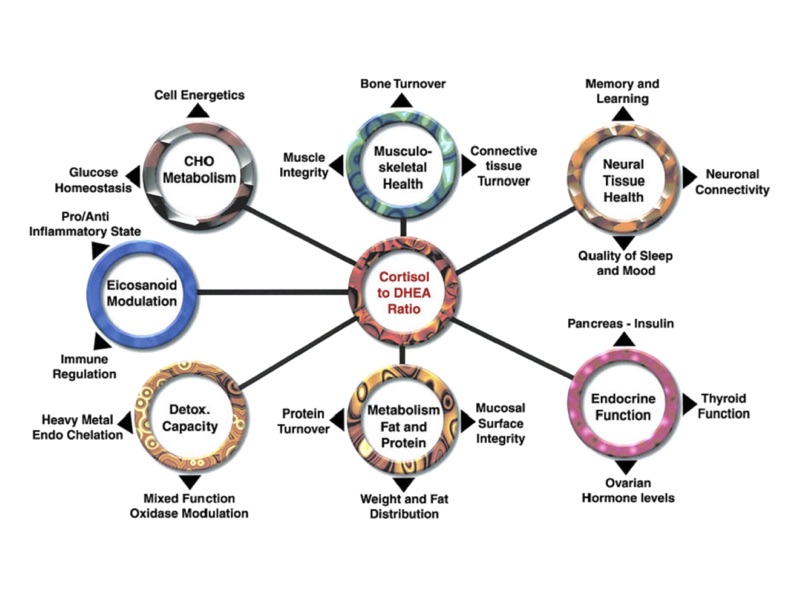
Aldosterone
- Secreted from the Zona Glomerulosa
- Functions of aldosterone include:
- Increases sodium retention throughout the body
- Increases potassium excretion
- Increases water retention
- Increases extracellular volume
- Enhances the activity of the sodium/potassium pump
- Helps “bring on line” the sodium and potassium channels in the luminal membrane in the kidneys
Glucocorticoid (Cortisol)
- Secreted from the Zona Fasciculata
- Functions of Glucocorticoid (Cortisol) Include:
- Mobilizes and increases amino acids in blood and liver by promoting protein catabolism
- Stimulates liver to convert amino acids to glucose
- Stimulates increased glycogen in the liver
- Inhibits glucose utilization in the peripheral tissue
- Mobilizes and increases fatty acids in the blood by supporting synthesis of hormone sensitive lipase
- Counters inflammation and allergies
- Prevents loss of sodium in urine and helps maintain blood volume and blood pressure
- Sustains tissue responsiveness to catecholamines
- Maintains resistance to stress
- Maintains personality and emotional stability
- Modulates thyroid function
Sex Hormones (DHEA)
- Secreted by the Zona Reticularis
- Functions of DHEA include:
- Acting as an androgen with anabolic activity
- Precursor to testosterone
- Precursor to estrogen and progesterone
- Reverses immune suppression caused by excessive cortisol level and therefore improves resistance to viruses, bacteria, candida albicans, parasites, allergies and cancer
- Functions of DHEA include:
- Stimulates bone deposition and remodeling, which can help prevent osteoporosis6.Improves cardiovascular status by lowering total and LDL cholesterol levels, lessens incidence of heart attack
- Increases muscle mass
- Decreases percentage body fat
- Reverses many of the unfavorable effects of excess cortisol and help create an improvement in: energy, vitality, sleep, PMS, and mental clarity
- Can help with quicker recovery from any kind of acute stress: insufficient sleep, excessive exercise, mental strain etc.
The Adrenal Medulla
- Contains chromaffin cells (also called phaeochromocytes)
- These cells are surrounded by a meshwork of blood vessels called venous sinusoids.
- The chromaffin cells, when stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system secrete noradrenaline and adrenaline into the sinusoids, which are delivered by the bloodstream to the rest of the body.